
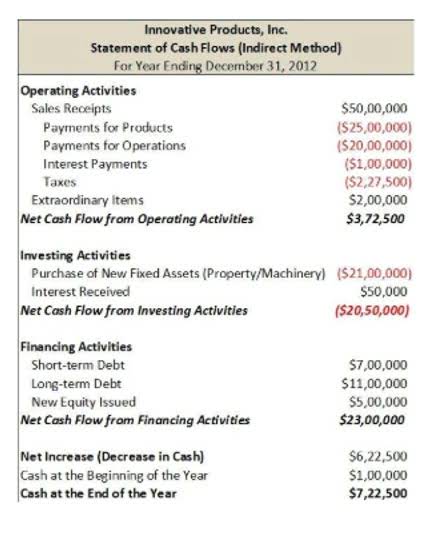
XYZ Ltd. manufactures a particular product (running at ~70% capacity) and sells at a net profit margin of 20%. However, XYZ ltd received an order which states the company will be able to make a net profit margin of 10%. However, if the company with its full capacity can supply the product, it may lead to a higher margin than its forecasted ~10%. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping.
Determine Relevant Figures
Understanding this cost component assists in fine-tuning production strategies, improving efficiency, and informing important pricing and investment decisions. On the other hand, fixed costs like rent and overhead are left out of incremental cost analysis since they don’t usually change with production volume. Additionally, fixed costs can be challenging to attribute to a specific business segment. Sunk costs, or past expenditures that cannot be recovered, must be excluded from incremental analysis. For example, if a company has already invested in specialized machinery now deemed obsolete, the initial investment is irrelevant to future decisions. Focusing solely on future costs and revenues prevents the “sunk cost fallacy,” where past investments irrationally influence current choices.

Real-life Examples of Incremental Cost Analysis

If the hypothetical removal of C had actually occurred, the unit FAC for the remaining eight units of A and B would have risen to €49 (an eighth of €392). This negative incremental cost means the company saves money with each additional table produced. Now let’s consider a mid-sized furniture manufacturer, Oak Wood Industries, that produces wooden tables. They are considering upgrading their production technology to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Identifying Incremental Costs in Your Business
To that end, in this study, we use the most comprehensive and recent evidence available on public health spending and health outcomes across Spanish regions. Incremental development approaches offer a flexible and adaptive method suited for projects with high uncertainty or evolving requirements. Unlike sequential models, incremental development delivers value in chunks by breaking down the system into manageable increments, each providing a subset of capabilities. This https://hopspilopper.dk/illinois-department-of-revenue/ allows for potential early deployment, faster feedback, and continuous improvement based on real-world insights. The article explores practical applications, planning challenges, and the importance of balancing a structured roadmap with flexibility. It also highlights the Incremental Commitment Spiral Model (ICSM), which integrates concurrent development and risk assessment to guide informed decisions across successive development cycles.
What Is Incremental Analysis?
- Understanding this cost component assists in fine-tuning production strategies, improving efficiency, and informing important pricing and investment decisions.
- The proposed approach has been applied for distributed optimization in a smart grid and simulation results under different scenarios are provided.
- However, the cost of potential bugs that may arise, leading to customer dissatisfaction and support costs, is much harder to predict and measure.
- For example, say a factory production line is at full capacity and therefore the company would like to add another production line.
- Unlike traditional costing methods that consider total costs, incremental costing focuses on the change in total cost resulting from a change in the level of activity or output.
The incremental cost of capital is calculated using methods such as the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) approach and the marginal cost of capital incremental cost approach (MCC) approach. Real-world examples illustrate how this concept is applied in practice, helping businesses and investors make informed decisions. By considering the incremental cost of capital, you can enhance your financial decision-making and increase the likelihood of success in your ventures.
- If the business decides to outsource then for each unit the direct manufacturing costs (12.00) and the variable overhead costs (4.00) will be saved.
- It excludes fixed overhead costs that don’t fluctuate with short-term changes in output.
- A manufacturing company produces a product at $5.5 per unit and sells at $7.5 per unit.
- By analyzing these incremental costs, the firm can allocate its resources effectively and maximize returns.
- Exploiting variations in health spending and health outcomes across regions and over time, in this study, we apply fixed-effect methods on a 20-year panel dataset.
- This approach streamlines processes, enabling organizations to minimize unnecessary expenditures while maximizing outcomes.
Incremental Cost: How to Calculate and Use It for Decision Making and Cost Benefit Analysis
- For a production manager, understanding these costs helps in optimizing resource allocation and operational efficiency.
- We follow a strict editorial policy, ensuring that our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts.
- The difference between the two decision methods results from the treatment of fixed costs.
- Since the fixed cost is being incurred regardless of the proposed sale, it is classified as a sunk cost and ignored.
- The 17 regions pertain to the 17 ACs that are responsible for planning and delivering health services to their populations in Spain and which hold over 92% of the overall national health budget.
If no excess capacity is present, additional expenses to consider include investment in new fixed assets, overtime labor costs, and the opportunity cost of lost sales. When a business operates near full capacity, incremental cost analysis becomes more complex due to production constraints. Increasing output often requires acquiring additional equipment, modifying supply chain logistics, or restructuring workflows. These changes can introduce cost increases that are not proportional to output due to inefficiencies or bottlenecks. It is closely related to incremental cost but focuses on a per-unit basis rather than the total additional cost of a decision.


For example, say a factory production line is at full capacity and therefore the company would like to add another production line. Incremental costs might include the cost of new equipment, the people to staff the line, electricity to run Bookkeeping vs. Accounting the line, and additional human resources and benefits. All these costs would be considered long-term incremental costs because they would be implemented as long-term aspects of the business. Accurate cost prediction and measurement is critical to properly pricing goods and services.